Disclaimer: The information in this article is for reference only. It is not a substitute for medical advice. Readers are encouraged to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance regarding their specific medical concerns and decisions.
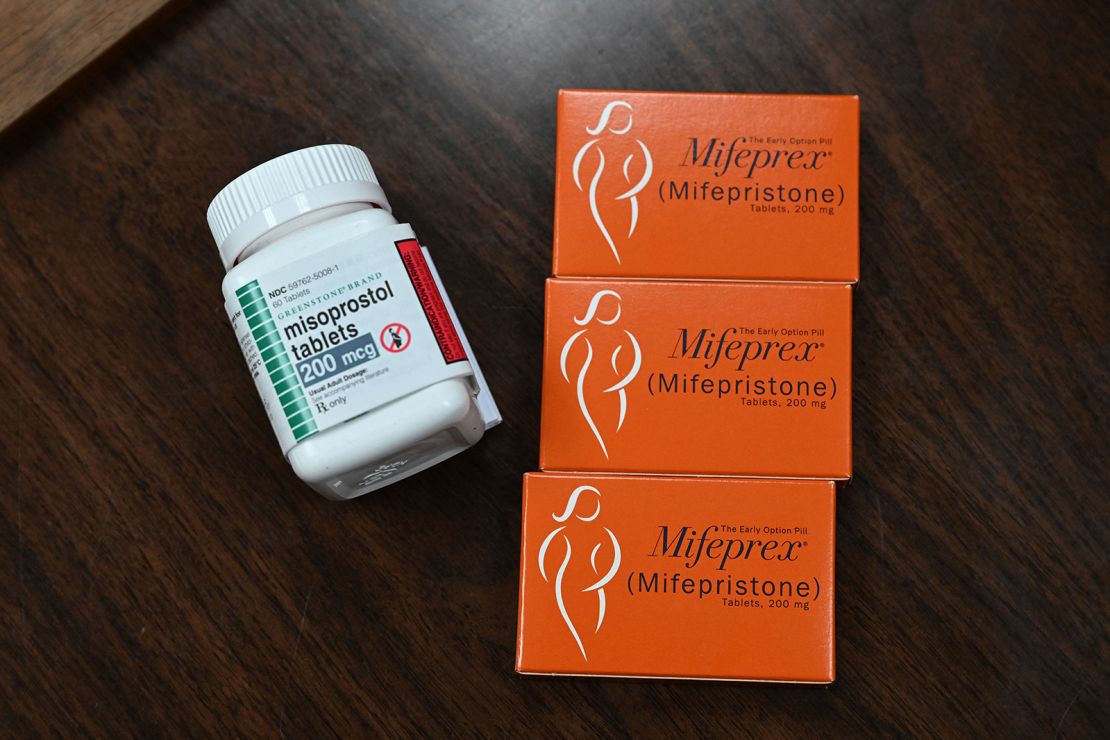
Comprising a combination of medications, namely mifepristone and misoprostol, this method offers individuals the option to undergo the abortion process within the privacy of their homes. Understanding how the abortion pill works and its implications is paramount for informed decision-making. This article delves into the mechanism of action of the abortion pill, shedding light on its efficacy, safety, and common misconceptions.
What is an Abortion Pill?
The abortion pill operates through a two-step process. Mifepristone, the initial medication, blocks the body’s production of progesterone, a hormone vital for sustaining pregnancy. This action prompts the detachment of the embryo from the uterine wall. Subsequently, misoprostol induces uterine contractions, facilitating the expulsion of the embryo, akin to a menstrual period. This combination effectively terminates the pregnancy within the comfort of one’s home, offering a discreet and accessible option for individuals seeking abortion.
How the Abortion Pill Works?
The “abortion pill” refers to a medication regimen used to terminate an early pregnancy. The most common medication regimen for medical abortion involves two drugs: mifepristone and misoprostol. Here’s how they work:
- Mifepristone: This is usually the first medication given. It works by blocking the hormone progesterone, which is needed for the pregnancy to continue. Without progesterone, the lining of the uterus breaks down, cutting off the blood supply and nutrients to the embryo or fetus. This essentially causes the pregnancy to detach from the uterine wall;
- Misoprostol: This is taken after mifepristone, typically within 24 to 48 hours. Misoprostol causes the uterus to contract and expel its contents, including the embryo or fetus. It softens and dilates the cervix, making it easier for the pregnancy tissue to pass out of the uterus.
The combination of these two medications is highly effective in terminating early pregnancies, typically up to around 10 weeks gestation. The process is similar to a miscarriage and usually involves bleeding and cramping as the uterus expels the pregnancy tissue.
It’s important for individuals undergoing a medical abortion to follow up with their healthcare provider to ensure that the abortion is complete and to address any concerns or complications. It’s also crucial to have access to emergency medical care in case of severe bleeding or other complications. Additionally, medical abortion may not be suitable for everyone, so it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to discuss the best options for each individual’s circumstances.
What happens if I take misoprostol orally?
Taking misoprostol orally can still induce uterine contractions and lead to the expulsion of the embryo, similar to other routes of administration such as vaginally or sublingually (under the tongue):
- However, oral administration of misoprostol may result in slower absorption and less predictable effectiveness compared to the recommended methods;
- It’s important to follow the prescribed protocol for medication abortion as directed by a healthcare provider to ensure safety and effectiveness.
If you have questions or concerns about the administration of misoprostol or any aspect of your abortion procedure, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance and support.
Addressing Misconceptions
Several misconceptions cloud the understanding of the abortion pill, leading to misinformation and uncertainty. One common fallacy is equating the abortion pill with the morning-after pill. While both serve contraceptive purposes, they are distinct medications intended for different scenarios. The morning-after pill, containing Levonorgestrel, acts as an emergency contraceptive to prevent pregnancy post unprotected intercourse, whereas the abortion pill terminates an existing pregnancy.
Another prevalent misconception revolves around the reversibility of the abortion pill. Despite claims suggesting reversal procedures, no conclusive evidence supports their efficacy or safety. However, studies indicate that abstaining from the second medication may decrease the likelihood of abortion completion, emphasizing the importance of informed decision-making and prompt medical consultation.
Furthermore, concerns regarding the safety of the abortion pill abound. Like any medical procedure, it carries inherent risks, yet both medical and surgical abortions boast a low incidence of major complications, underscoring their safety under proper medical supervision.
Accessing the Abortion Pill
Obtaining the abortion pill requires consultation with a healthcare provider at a clinic, medical office, or hospital. Purchasing it online poses significant risks, as authenticity and medical support cannot be guaranteed. Individuals facing unplanned pregnancies should promptly contact their healthcare provider to discuss their options. The FDA-approved timeframe for utilizing the abortion pill extends up to 10 weeks after the last menstrual period, offering a window for informed decision-making and access to safe healthcare practices.
Conclusion
Understanding the mechanism and dispelling misconceptions surrounding the abortion pill are essential steps towards informed decision-making for individuals considering this option. By elucidating its function and addressing prevalent myths, we empower individuals to navigate their reproductive choices with clarity and confidence. Accessing the abortion pill through proper medical channels ensures safety and support throughout the process, underscoring the importance of timely consultation and informed healthcare decisions.
The abortion pill represents a significant advancement in reproductive healthcare, providing individuals with autonomy and privacy in their decision to terminate early pregnancies. By inhibiting the production of progesterone and inducing uterine contractions, mifepristone and misoprostol work in tandem to effectively end pregnancies. Dispelling misconceptions surrounding the abortion pill is crucial for ensuring informed decision-making and access to safe healthcare practices. As individuals navigate their reproductive choices, seeking guidance from qualified healthcare providers and understanding the facts about the abortion pill empower them to make decisions aligned with their values and circumstances.